Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokomura, Ryota*; Goto, Masataka*; Yoshida, Takehito*; Warisawa, Shinichi*; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Fukui, Rui*
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (Internet), 9(4), p.3275 - 3282, 2024/04
To reduce errors in the remote control of robots during decommissioning, we developed a Rail DRAGON, which enables continuous observation of the work environment. The Rail DRAGON is constructed by assembling and pushing a long rail structure inside the primary containment vessel (PCV), and then repeatedly deploying several monitoring robots on the rails to enable constant observation in a high-radiation environment. In particular, we have developed the following components of Rail DRAGON: bendable rail modules, straight rail modules, a basement unit, and monitoring robots. Concretely, this research proposes and demonstrates a method to realize an ultralong articulated structure with high portability and workability. In addition, it proposes and verifies the feasibility of a method for deploying observation equipment that can be easily deployed and replaced, while considering disposal.
Nakamura, Keita; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Baba, Keita*
Artificial Life and Robotics, 28(2), p.352 - 360, 2023/02
Kurata, Masaki; Okuzumi, Naoaki*; Nakayoshi, Akira; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.807 - 834, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:95.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Immediately after the 1F-accident, various attempts have been made to evaluate the fuel debris characteristics toward the decommissioning of 1F. The present review outlines those attempts. In the years immediately following the 1F-accident, the knowledge obtained from the 1F-site (especially from the damaged reactors of Units 1, 2 and 3) was extremely limited. The approximate location of fuel debris was investigated by muon tomography, and its characteristics were roughly estimated based on the past findings such as the results of the Three Mile Island-II accident investigation in the United States, which gave us information of prototypical accident scenarios and debris characteristics for pressurized water reactor accident. After that, various internal investigation robots were developed, and from 2017, investigation of the inside of the reactor containment vessel was started using these robots. Consequently, these three units were found to have core damage status and debris distribution that were rather different from what had been expected based on the typical accident scenario of a pressurized water reactor. In parallel, a small amount of U-bearing particle was recovered from the smear samples of these robots. The analysis of these particles is ongoing to get information relevant to fuel debrsi body. Furthermore, international collaboration is ongoing mainly under OECD/NEA, including accident analysis and debris characterization. From now on, one need to further understand 1F-accident scenario and progress debris characterization based on these 1F-site information.
Wakai, Satoshi*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.491 - 496, 2021/12
After Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, various corrosion mitigating activities have been treated, and severe corrosion incident have never taken placed. On the other hand, the facilities were exposed sea water, and some of them have continuously exposed to ground water. The exposure of metal materials to environmental water has a risk of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). In this paper, we summarize the latest knowledge of MIC and the task of MIC in the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Kino, Chiaki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111256_1 - 111256_19, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to grasp the long-term distributions of FP as well as fuel debris all over the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) for safe completion of its decommissioning projects. The fuel debris is going to be removed from the plant under the severe conditions of FP being scattered during major decommissioning work, and then, the decommissioning projects are going to be terminated by storing safely the removed debris as recovered fertile materials or as materials for final radioactive disposal. In order to determine the FP distribution in the plant for the long period from the accident occurrence to the termination of the plant decommissioning, procedures for analyzing multi-term FP behaviors were proposed. The proposed procedures should be improved by applying the FP data measured in the plant and validated based on the feedback data. Then, the accuracy-improved procedures should be applied to estimate FP distribution during each period of the decommissioning projects.
Kawabata, Kuniaki
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(5), p.050501_1 - 050501_9, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:18.54(Physics, Applied)This paper describes the decommissioning work being undertaken at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings Inc.'s (FDNPS) using remote controlled robotic systems, as well as lessons learned from past remote task executions. We also summarize the issues to be considered in promoting safe, steady, and efficient decommissioning based on past experiences. In response to these issues, we are developing test methods for performance evaluation of the robots for nuclear decommissioning, robot simulator for operator proficiency training, and information generation methods to improve the operator's status awareness. The current status of technological development is also described.
Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo 2020 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.9 - 16, 2020/05
The author has been continuing research and development for corrosion science for about forty years. One of the main targets of his research is applying computational science techniques on corrosion problems. The results are briefly introduced in this article. Also, the author organized some workshop for corrosion problems of 1F decommissioning procedure for several years. Such activities are evaluated for receiving the society award in JSCE.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Tadokoro, Takahiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai-Shi, 122(1211), p.18 - 20, 2019/10
no abstracts in English
Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/05
The decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident is one of the most important issues in Japan. The criticality safety of fuel debris is imperative to prevent exposure of workers. The investigating criticality monitoring system cannot detect the criticality of fuel debris quickly. The estimation of criticality of fuel debris is required for the fuel debris retrieval. Though the expert knowledge of reactor physics is necessary to estimate the criticality of fuel debris, many people who make a plan of fuel debris retrieval may not know well about criticality analysis. We developed a handy criticality analysis tool HAND to quickly estimate the criticality of fuel debris without expert knowledge of reactor physics. Since the input data of HAND is so simple and users can intuitively understand the calculation results, this tool is expected to be the effective tool to estimate the criticality of fuel debris.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Takano, Masahide
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.200 - 203, 2018/11
Chemical state of some simulated corium debris samples containing uranium (fuel), zirconium (fuel cladding), iron (structure material), calcium (cement) and lanthanides (fission products) was investigated by synchrotron radiation based extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis. The local structure of uranium for the simulated debris was classified into fluorite UO structure and C-type structure (stabilized cubic). The U
structure and C-type structure (stabilized cubic). The U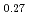 Zr
Zr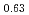 Fe
Fe Ca
Ca O
O sample, which consists of single phase (C-type), shows slightly shorter U-O distance. It can be concluded that the sample contains pentavalent uranium. The local structure of zirconium for U-Zr-O and U-Zr-Fe-O systems was very close to tetragonal ZrO
sample, which consists of single phase (C-type), shows slightly shorter U-O distance. It can be concluded that the sample contains pentavalent uranium. The local structure of zirconium for U-Zr-O and U-Zr-Fe-O systems was very close to tetragonal ZrO , while that of zirconium changed to CSZ (calcia stabilized cubic) by adding calcium.
, while that of zirconium changed to CSZ (calcia stabilized cubic) by adding calcium.
Miyamoto, Yasuaki
Nihon Robotto Gakkai-Shi, 36(7), p.464 - 467, 2018/09
I introduced the activities of Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, the summary of the CLADS Main Building and main result.
Kawabata, Kuniaki; Mori, Fumiaki*; Shirasaki, Norihito; Tanifuji, Yuta; Hanari, Toshihide
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII 2017), p.450 - 455, 2018/02
This paper describes the test facilities and experimental environments for supporting the decommissioning of the nuclear facilities especially Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station by remote operation. Naraha Remote Technology Development Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an institution for such purpose. Mock-up staircase, robot testing pool and motion capture arena are already installed and full service and support began from April, 2016. We are also designing and developing some experimental environment for remotely operated robots for nuclear decommissioning. In this paper, we describe current status and development of test facilities of Naraha Remote Technology Development Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Miyachi, Shigehiko
Enerugi Rebyu, 37(10), p.19 - 20, 2017/09
The JAEA is currently constructing the Okuma Analysis and Research Center near the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station site. These are consists of three buildings; Administrative building and hot laboratories; Laboratory-1 and Laboratory-2. Radioactive analysis in hot laboratories will provide the data needed to establish the strategy and methodology for treatment and disposal of radioactive rubbles, and for the removal methods of fuel debris in the reactors.
Kawabata, Kuniaki; Suzuki, Kenta; Isowa, Mitsuru*; Horiuchi, Kazunori; Ito, Rintaro
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.561 - 564, 2017/06
This paper describes the current status of the development of a simulation system for remotely operated robots. The system will be used for operator proficiency training and robot performance verification. Our purpose for developing this system is to contribute to decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The simulator system was designed using Choreonoid, a simulator development tool. The effects of view disturbances, communication failures, and so on are extended functions that are implemented on the simulator. The effects of water submergence on the physical behavior of underwater robots are also implemented. In this paper, we introduce the prototype of the robotic simulator system with the newly implemented extended functions. Some examples of system output are shown.
Daido, Hiroyuki
Reza Kenkyu, 45(3), p.135 - 136, 2017/03
I describe how important the challenge to Fukushima Daiichi and recovery of this area. From this point of view, scientific and technological trials originated from the disaster and accident should be based on the mission of Fukushima recovery.
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki
Gijutsushi, 28(10), p.4 - 7, 2016/10
For decommissioning the Fukushima-Daiichi Power Plant, various studies and activities have continued. In this paper, it was mainly described the status of research for fuel debris retrieval with remote technologies, which was the most difficult challenge, introduced in CPD program. Investigation and analyzing for debris condition in each reactor have done. Various researches and developments for the way of fuel debris retrieval with remote technology, including in access route, from the top or side, have continued with the result.
Yanagihara, Satoshi
Science & Technology Journal, 11(10), p.22 - 23, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Okoshi, Minoru
Radioisotopes, 47(5), p.412 - 423, 1998/00
no abstracts in English